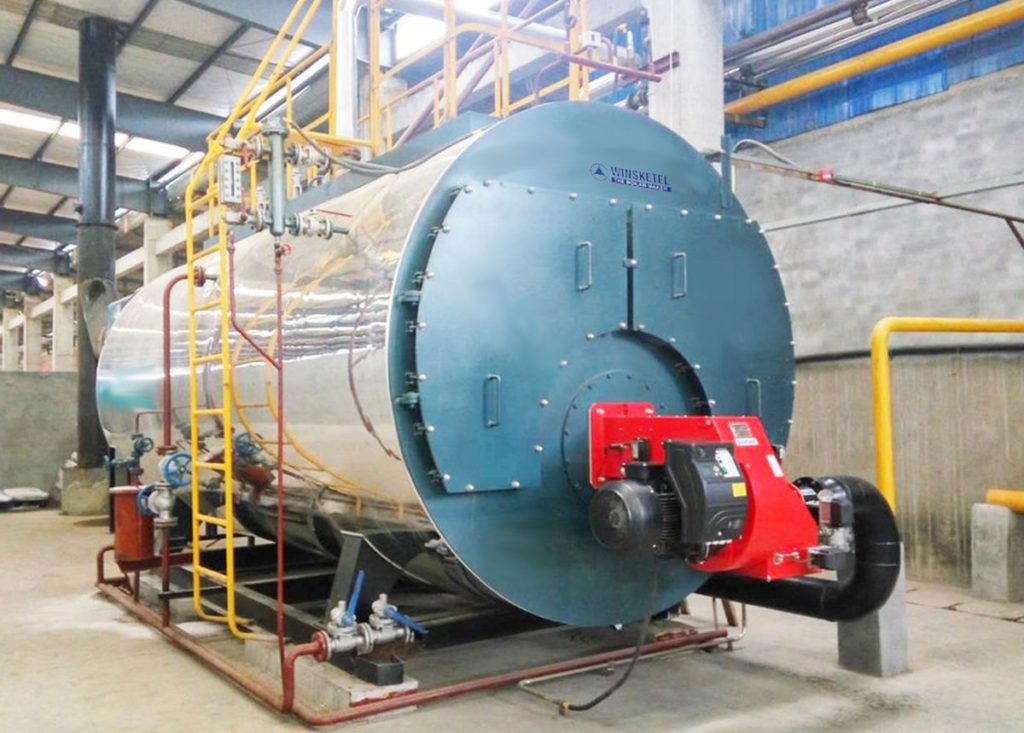
To manufacture safe food, many processing aids are used. One such underrated aid is the boiler. Despite being a ubiquitous part of food industry, it is given very little importance. From processing / cooking to cleaning, steam in food manufacturing is used as it is the most efficient method of heat transfer. Steam offers precise temperature control through relatively simple, inexpensive pressure control to deliver consistent heat across even the largest of vessels. It also offers the precision to ensure that the food produced is of the highest quality for the manufacturers’ end-user consumers.
In simple terms boiler is defined “as a closed vessel in which water or other liquid is heated, steam or vapor is generated, steam is super-heated, or any combination thereof, under pressure or vacuum, for use external to itself, by the direct application of energy from the combustion of fuels, from electricity or nuclear energy.“

According to Indian Boiler Regulation 1950, “Boiler” means any pressure vessel exceeding 22.5 litres (five gallons) in capacity which is used expressly for generating steam under pressure and includes any mounting or other fitting attached to such vessel, which is wholly or partly under pressure when steam is shut off.
Food processing units require hot water and steam that is produced by the boiler. It has diverse applications:
- Sterilizing food products
- Ingredient in food like culinary steam
- Cleaning & Sanitizing lines & equipment
- Hot Water Generation for Sanitation
- Hot Water for Facilities
- Steam Power for Machinery
- Heating Requirement for Facility
- Steam for Batching
- Steam for Processing
- Steam for Cooking
- Steam for Drying Food
- Steam & Heat for Packaging
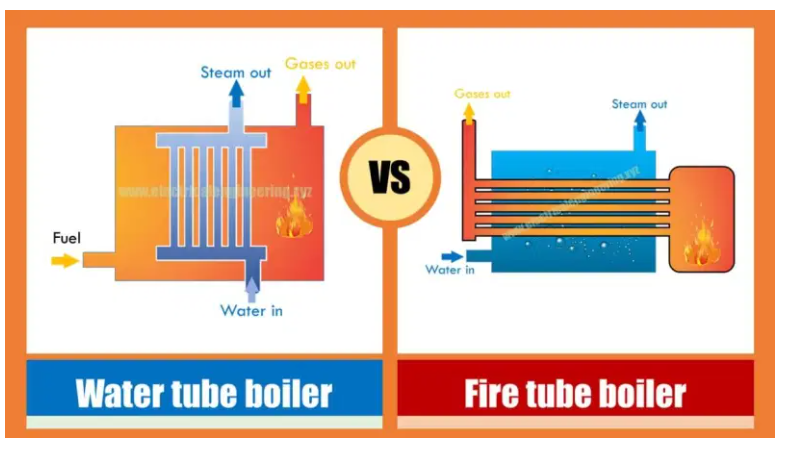
Based on the designs, boilers are broadly classified into fire and water tube boilers with water tube boilers being a more popular choice because of their efficiency and low risk to human safety. Each boiler requires fuel, such as nuclear fuel, oil, natural gas, flue gas, wood or other biodegradable fuel to operate.
For the right boiler size and pressure, it is imperative to determine how much steam and hot water consumption the plant requires. Based on this, the boilers are categorized into low, medium, and high pressure.
How to choose a boiler for your plant?
While steam heat serves many purposes in the food processing industry, the boilers themselves often present their own challenges. Most of the food manufacturing units do not require 24/7 steam. Boilers usually take a lot of time heating up and cooling down. This, of course, results in lowered energy efficiency and higher fuel costs. Therefore it is important to focus on some key points while choosing the boiler for your plant.
- Adaptable to demands: Steam requirements in a food processing plant may differ largely depending on the tasks. Some days or certain times of a day can be busier than others. A boiler system that can power up and down quickly will help prevent operations from being interrupted when demand increases, saving on fuel costs when steam is not needed.
- Fuel and water efficiency: Rising fuel and water costs can quickly complicate budgets and start digging into profits, so it’s essential to find a boiler that can help with energy efficiency and conserving resources without sacrificing productivity. Companies in certain areas also face certain emissions restrictions, so a boiler rated to reduce harmful greenhouse emissions is a definite plus.
- Easy maintenance: With so much depending on the boilers, we definitely need the ones which are low on maintenance and have easy self diagnostics.
Regulatory Requirements
In accordance with the Indian Boiler Regulation 1950, a boiler is required to meet the following requirements:
- Material conformity of boiler, steam pipe, economizer, superheater, valves, and other boiler parts. In addition, the ASME boiler and pressure vessel code, TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association), TRD (Technische Regeln für Dampfkessel), JIS codes and other international standards can also be referred to as applicable.
- Approved design and drawings of boiler and boiler component
- Welder certificate for welder issued by the competent authority approved by Central Boilers Board
- Construction of boiler and testing under the supervision of Inspecting officer appointed by the state government
- Application of recognition for all the manufacturing works
- Register no. provided by the chief inspector inscribed on the boiler. Its removal is punishable with fine
- Annual inspection after boiler installation by Boiler Inspector
- Class I or II certificate for boiler attendant
- In case, Boiler is transferred from one state to another it should be communicated to the state government
- In case of accidents, within 24 hours owner will share the details
Once installed, proper operation and maintenance of the boiler are very important. To ensure smooth operation boiler water, feed-water, and cleaning chemicals, such as antiscalants, inhibitors, should be of suitable quality. BIS standards for the same are as follows:
| BIS Standard No. | Standard Name | Details |
| IS 10391:1982 | Code of practice for chemical cleaning of boilers | Guidelines for chemicals cleaning, according to deposit cleaning agent and inhibitors recommended |
| IS 10391:1982 | Specification for feed water and boiler water for low and medium pressure boilers | Specification which includes TDS, PH and other requirements for boiler of pressure not more than 5.9MN/m2 |
| IS 10496:1983 | Specification for feed water, boiler water and condensate for pressure Boilers | Specification which includes TDS, PH, and other requirements for boiler of pressure more than 5.9MN/m2 |
| IS 10500:2012 | Drinking Water – Specification | Prescribes the requirements and the methods of sampling and test for drinking water/potable ` |
In case if the steam and hot water are to come in direct contact with food or food contact surfaces, only potable water should be used in boilers. Planned cleaning schedules, appropriate chemicals, and inlet water reduce or eliminate the need to dismantle the boiler frequently, save energy, and reduce boiler malfunctions.
Information and implementation play an instrumental role in ensuring not only quality and safety of food manufactured, but also human safety.

Author: Disha Majhi, is a Senior Associate Consultant at Food Safety Works. She is an expert in the milk/dairy segment and cares deeply about the environment impact of the packaging.