The food consumption pattern in India is gradually getting diversified. Livestock products are of utmost importance in this diversified menu. There are numerous recipes that require eggs to be added but how safe is it to consume eggs without cleaning them? Should the eggs be washed or sanitized before consumption
FSSAI defines Egg as “eggs-in-shell other than broken, incubated or cooked eggs, laid by poultry species or birds meant for direct human consumption or the preparation of egg products.”
Eggs can taste and smell fine, but they may still have harmful microorganisms. Certainly, the dirt on the egg is generally organic material including fecal matter which may have harmful bacteria.
It is important to note that the quality and appearance of eggs depend mostly on storage and the length of the storage period.
Shelf life of an egg: Eggs keep their freshness for up to 10 to 12 days after they have been laid at room temperature of 280 C ±20 C, but the shelf life shortens with higher temperatures. Eggs can lose as much quality in one day at room temperature as compared to the days in the refrigerator.
The risks associated with eggs:
Eggs are among the nutritious foods and can be part of a healthy diet. But there are a lot of risks associated with it and to be safe, eggs must be safely handled as unbroken, clean, fresh.
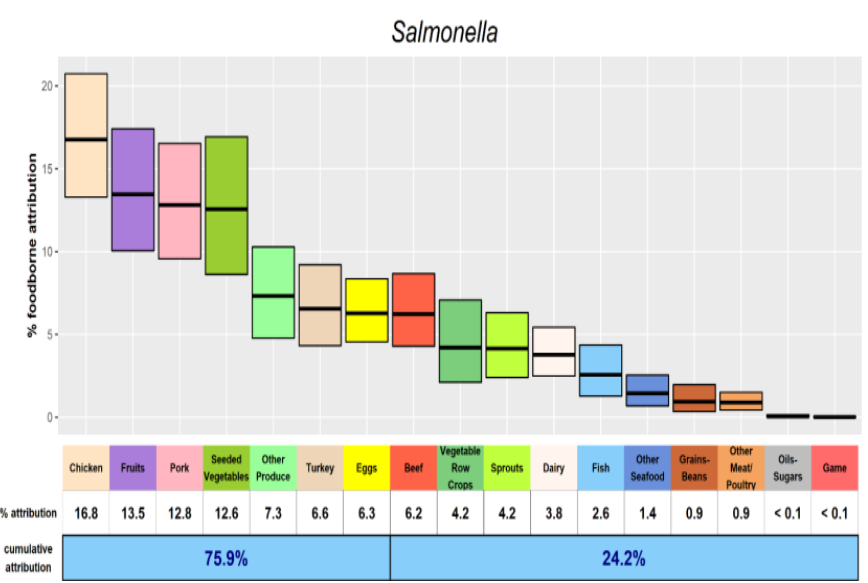
Figure: Estimated percentage of foodborne salmonella illnesses (with 90% credibility intervals) for 2019, in descending order, attributed to each of 17 food categories, based on multi-year outbreak data, * United States.
Shell eggs may have Salmonella enteritidis (SE) bacteria that can cause foodborne illness.
A report was released by Interagency Food Safety Analytics Collaboration (IFSAC) about foodborne illness outbreak sources in the United States in 2019 for Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and two other microorganisms. Among the annual reports of IFSAC, this was the first time in which Listeria illnesses were also attributed to either Other Produce or Eggs.
More than 75% of Salmonella illnesses were attributed to seven food categories: Eggs, Chicken, Fruits, Pork, Seeded Vegetables (such as tomatoes), Other Produce (such as nuts), and Turkey.
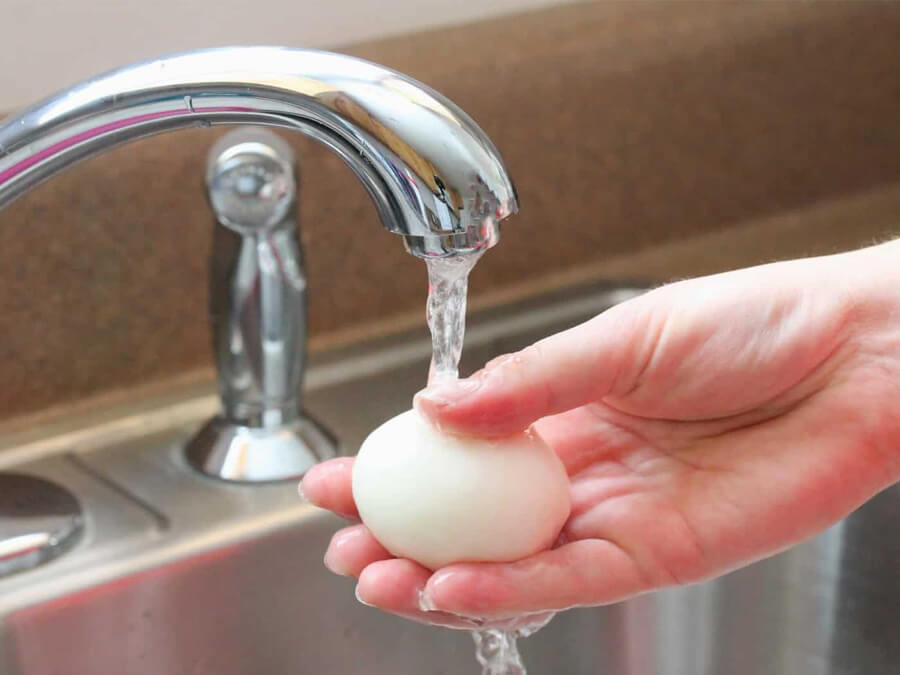
Is washing or cleaning of eggs necessary?
Before taking a call on whether the eggs must be cleaned or not, we should first have to understand the basics of the egg’s structure.
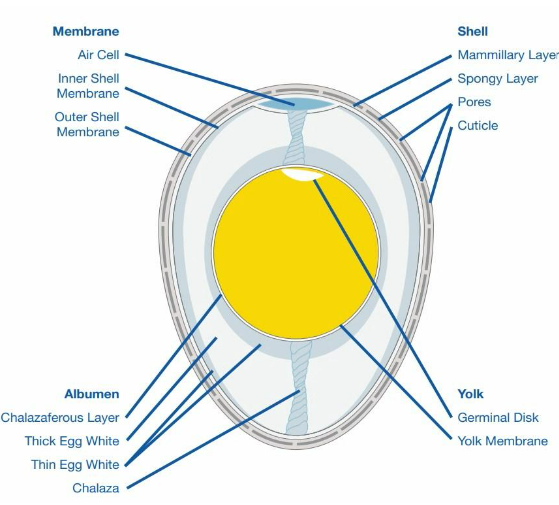
The egg has a cuticle as a topmost layer where it is made of a protein layer that covers the surface of the egg and fills the pores that allow the air inside for the growing chick. The purpose of the cuticle is to prevent the bacteria from entering the egg and to form the first line of defense against infection.
Bacteria can be present on the outside of an Eggshell because the egg exits the hen’s body through the same passageway as feces is excreted.
Considering cuticles, the washing of eggs may damage the cuticle and eventually leave the eggshells porous. This process may affect the eggshell cuticle layer and may allow the harmful bacteria to enter the eggs increasing the risk of contamination as the wash water can seep into the egg through the pores in the shell.
Various rules that are followed by the different countries regarding egg washing or cleaning:
India– The Food Safety Standard Authority of India released a guideline note on the handling of Eggs where they mentioned that they must not be washed because they become porous when washed. The FSSAI’s take on this is to avoid washing dirty eggs as it becomes more porous when wet and pave the way for bacteria to enter the egg. In the guidance document, It is also recommended to discard the dirty eggs.
European Union: EU regulations emphasize not to wash eggs because such practices can cause damage to the eggshell, which is an effective barrier to bacterial ingress with an array of antimicrobial properties. However, some practices, such as the treatment of eggs with ultra-violet rays, should not be interpreted as constituting a cleaning process.
USDA- United States Government regulations require that USDA-graded eggs be carefully washed and sanitized using only compounds meeting FDA regulations for processing foods. All USDA-graded eggs and most large volume processors follow the washing step with a sanitizing rinse at the processing plant.
Eggs are sometimes washed to remove extraneous material, which may include faeces, from the egg surface. In the commercial setting, this usually involves passing the egg through a series of sprays having detergents and/or sanitizing agents, followed by rinsing, drying, and oiling.
In a publication released by public health and safety of eggs and egg products in Australia, it was mentioned that, if the washing process is performed correctly, commercial egg washing results in a reduction in the level of microorganisms on the egg surface. Factors that are critical to the effectiveness of egg washing include the correct use of detergents and sanitizing agents and the use of proper wash water temperatures. Alternatively, if performed incorrectly, washing can increase the potential for transmission of Salmonella from the shell surface into the egg contents.
Egg-associated illness is a serious public health problem. Infected individuals may suffer mild to severe gastrointestinal illness, short-term, or chronic arthritis, or even death.
Proper handling of Eggs-
DOs √
- Retailers and traders must source eggs from credible sources and store them in refrigerators.
- Store eggs in refrigerators on designated shelves or in egg crates.
- Appropriate temperature and relative humidity (RH) need to be kept for storing eggs in the cold store, the lack of which can result in mixing up of the yolk and albumin.
- Consumers must buy eggs from stores that store eggs at cooler temperatures.
- Always wash your hands with soap and water after handling eggs.
- Consumers can make use of the guidance document to check the freshness and quality of eggs easily at home with the help of simple tests
DONTs ×
- Eggs must not be left in vehicles or in places where it can be affected by the hot atmosphere.
- Do not use cracked or dirty eggs and dispose of cracked and dirty eggs immediately.
- Avoid washing dirty eggs until necessary as they can become more porous when wet and this can pave the way for bacteria to enter the egg.
Implementing preventive measures like ensuring a clean and hygienic processing environment along with personal hygiene would reduce the number of infections from eggs.






